6. To publish
Publishing consists of transforming a document into a format suitable for its dissemination, via a style sheet that defines its final graphic appearance.
| Custom layouts | |
|---|---|
|
Advanced style sheets are not customized by default. They are provided by NeoDoc on demand for a specific layout and data transformation. |
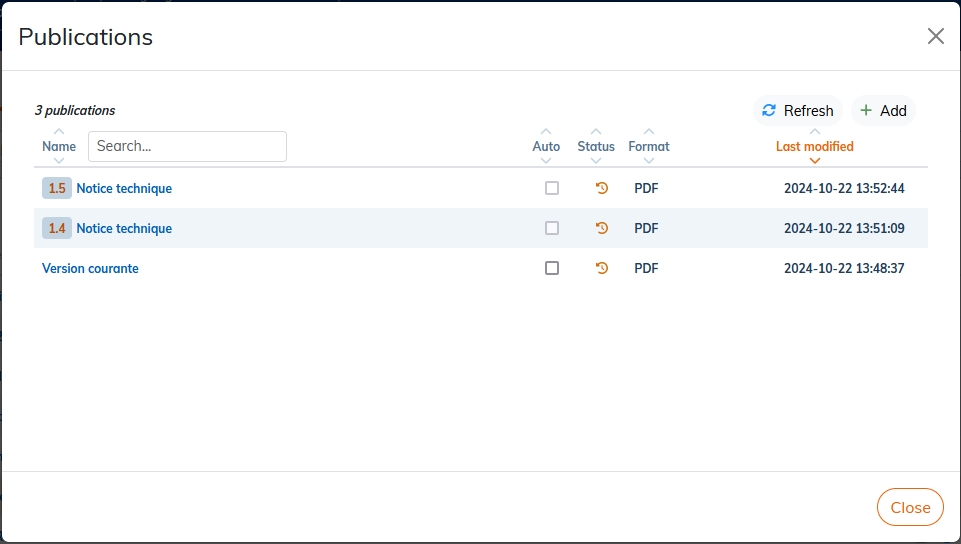
6.1. To create a publication
|
The instructions below concern the publication of the current version of the document. To publish a specific version of a document, see To publish a particular version. |
| Publications of a document created from a template | |
|---|---|
|
The publications defined on a template are automatically recreated on the instances of this template (Create a content template). |
-
Click on the
 icon corresponding to the document.
icon corresponding to the document.
-
Click on .
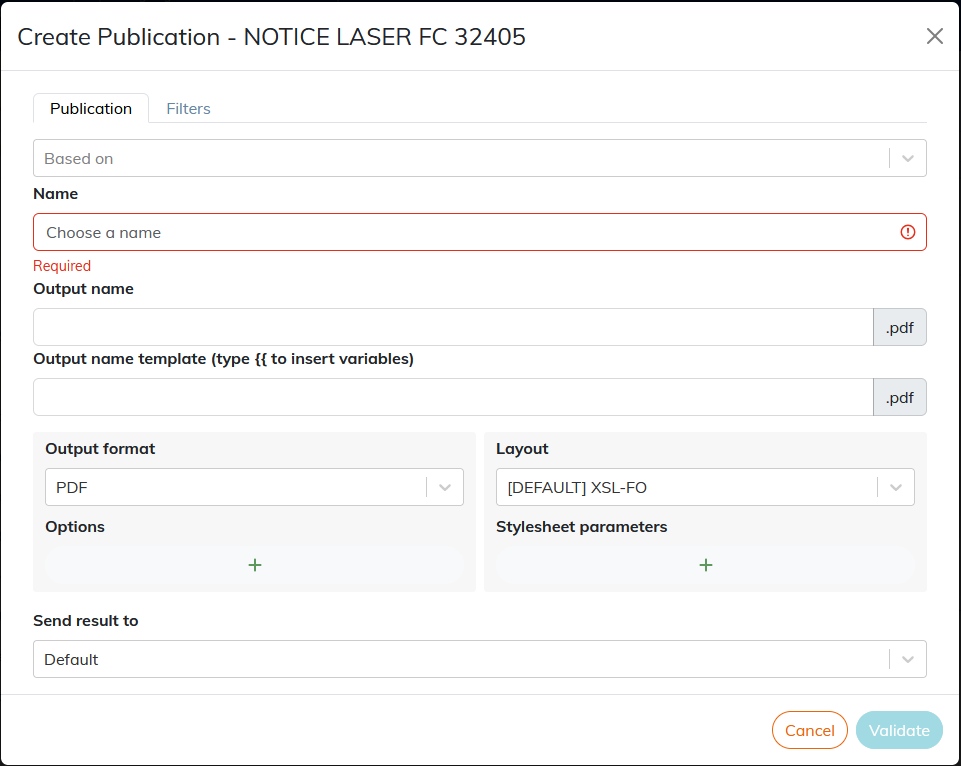
Procedure 9. To create a publication based on another publication
-
Click in the Based on field, select an existing publication.
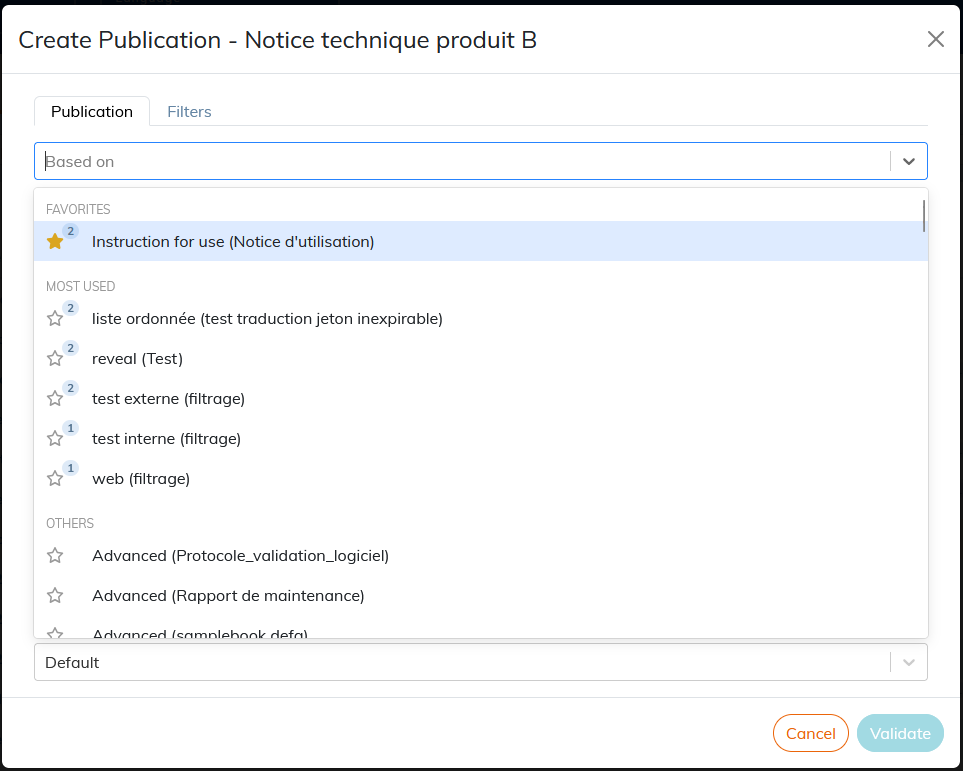
The name of a template publication is composed of [Publication name (document label)].
By default, all publication templates are in the “Others”. As they are used, the most widely used model publications make up the section “Most Used”.
The number next to the star indicates the number of times this publication has been used as a template.
You can click on the star to set the model publications as favorites.
-
In the field Name, the file name is automatically set with the name of the field Based on. Rename the publication if you want.
-
All parameters in the template are auto-populated. Set a Output Name Template if necessary.
-
Click Validate.
Procedure 10. Create a publication with manual setup
-
Skip the field Based on and enter a name to identify the post.
-
Select an output format in the drop-down list.
-
If necessary, select a layout format.
-
Click Validate.
|
Filters. The values selected in the “Filters” are to be applied for targeted publication (see To define the filtering criteria of a publication). |
|
For more advanced publication settings, refer to To configure a publication. |
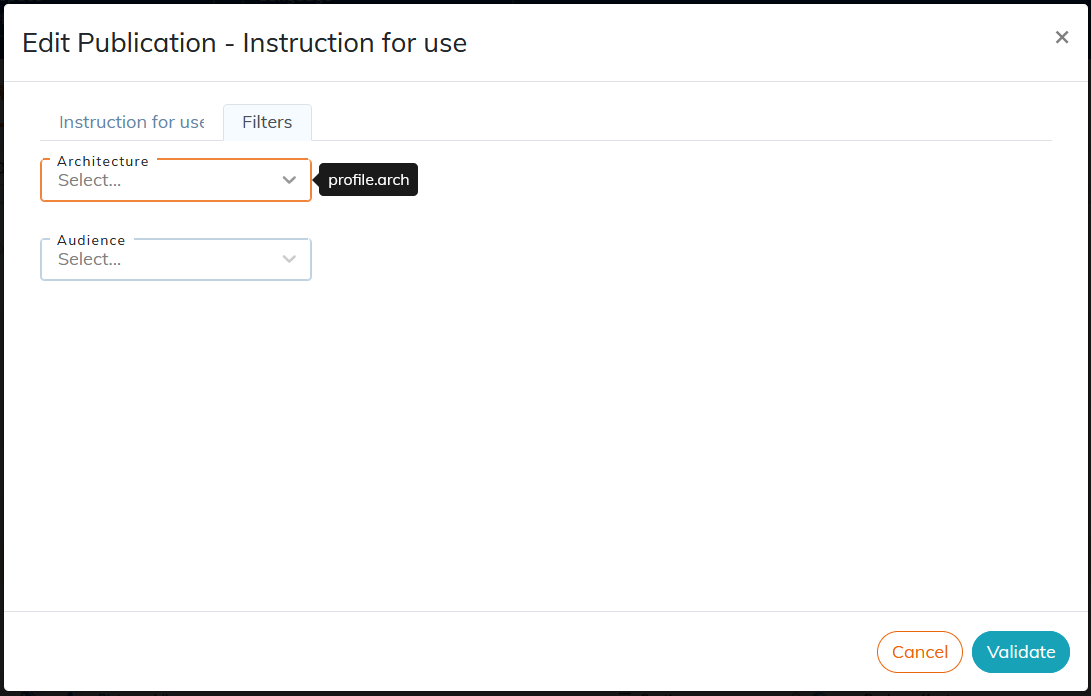
6.1.1. To filter content
This feature allows you to filter elements that do not match the goal of the publication. This makes it possible, for example, to generate two versions of the same document intended for two audiences who do not need exactly the same information.
The three stages of filtering
-
Customize attributes and set their values To customize attributes;
Customizing workspace-level attributes has no impact on content that is already profiled.
-
To profile elements (To profile);
-
To configure publications To define the filtering criteria of a publication.
6.1.1.1. To define the filtering criteria of a publication
The customized attributes are listed and their values can be selected without risk of error:
|
Document content items that do not have any filter criteria are published normally. |
6.1.1.2. Filtering rules and profiling restrictions
For a targeted publication to generate successfully, the filtering information set for a publication and the profiling information set at the content level in the editor must be consistent.
See the most common restriction cases and methods for detecting potential issues impacting publications Detect potential issues related to profiling.
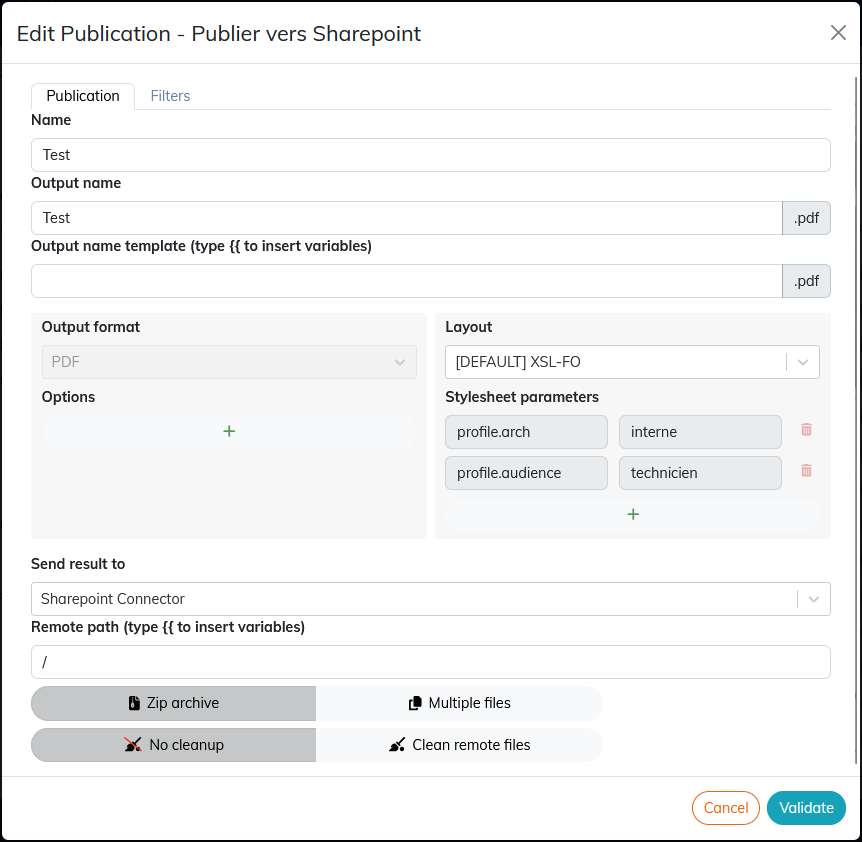
6.1.2. To configure a publication
|
|
For advanced users, this window will allow to modify all the possible parameters of the publication: Name
Output Name and Output Name Template The output name is assigned to a publication when it is downloaded or sent to an external server (see Send result to). By default, the output name is the same as the name. The output name can be configured:
The available variables are:
For example, by setting the Output format
Options The options are specific to each output format. Main options are:
Layout
Parameters of a style sheet
Send result to
Remote path
|